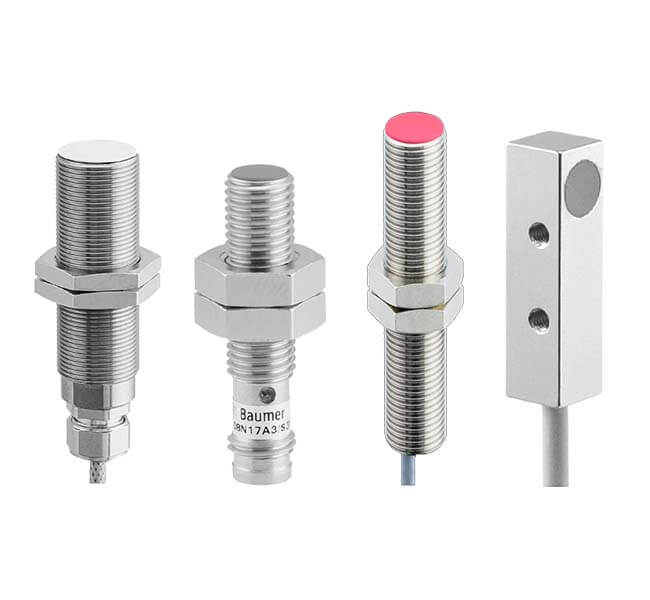
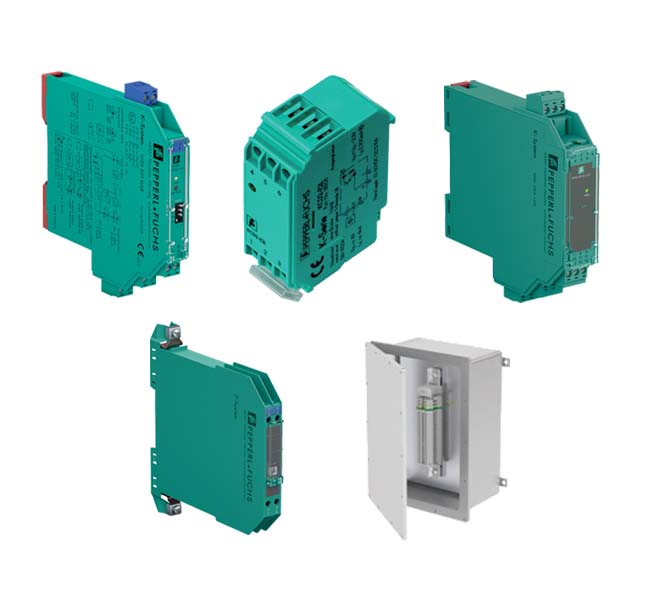
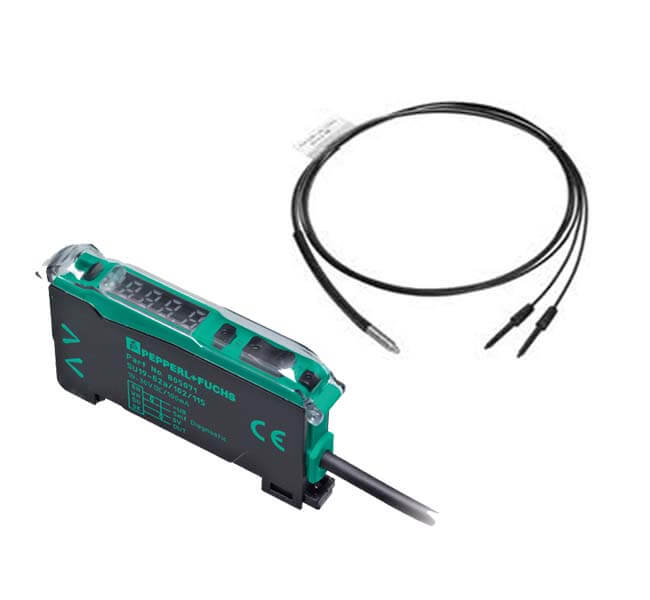
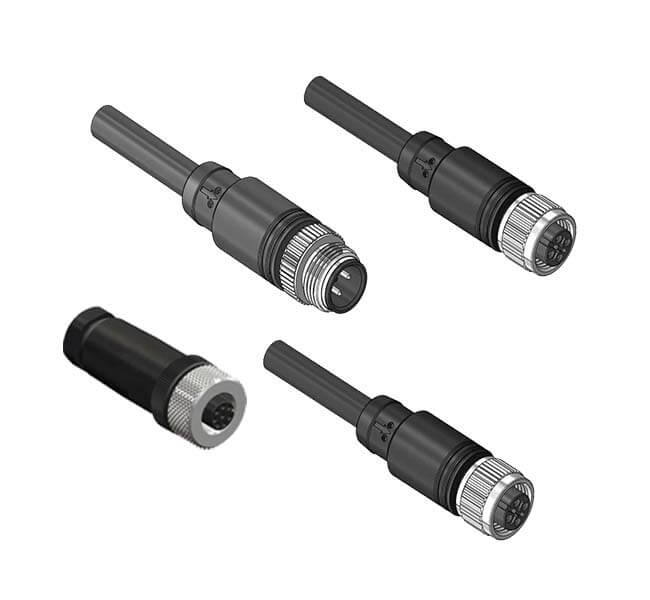
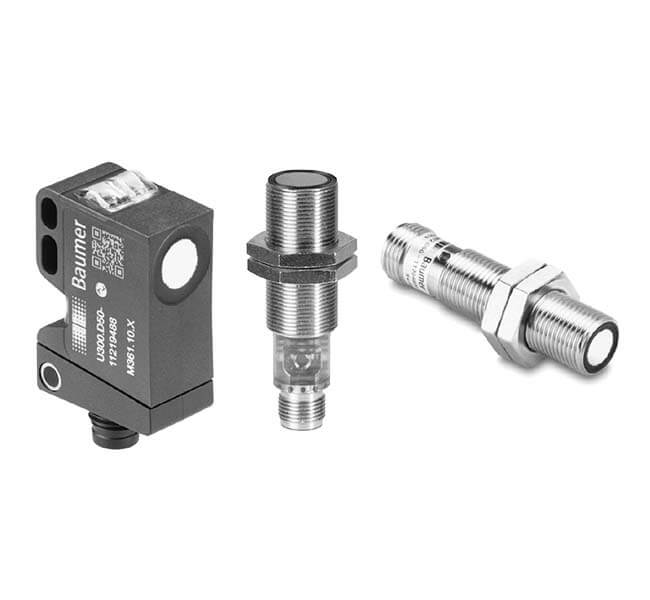
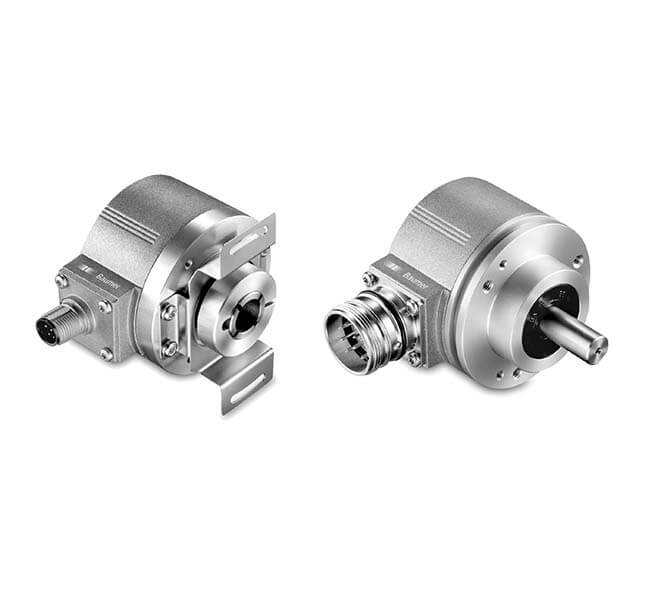
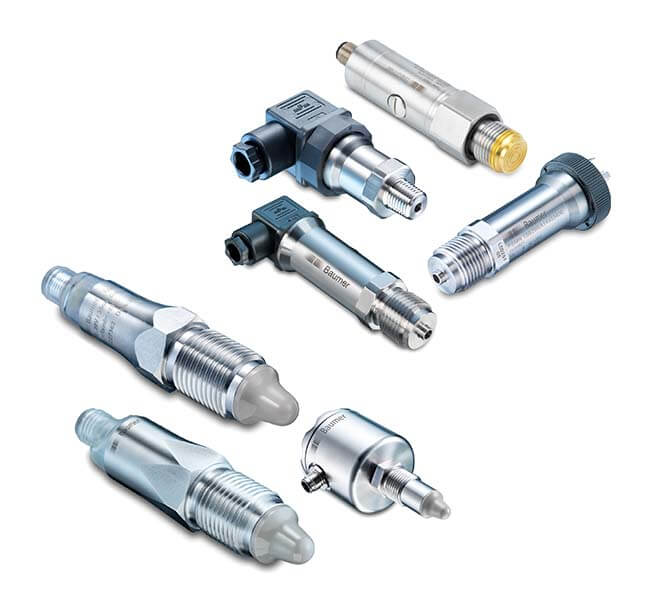
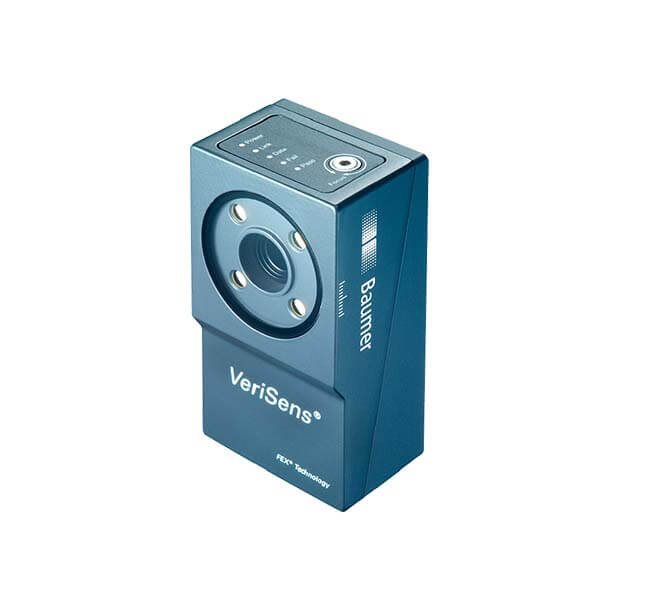
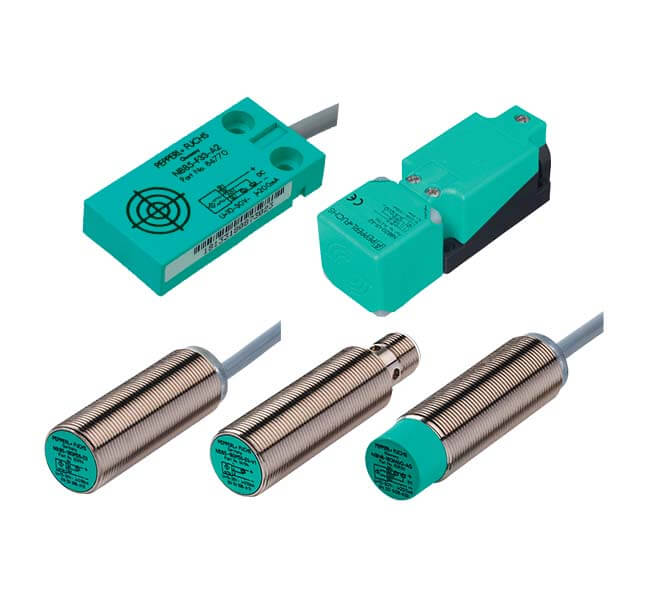
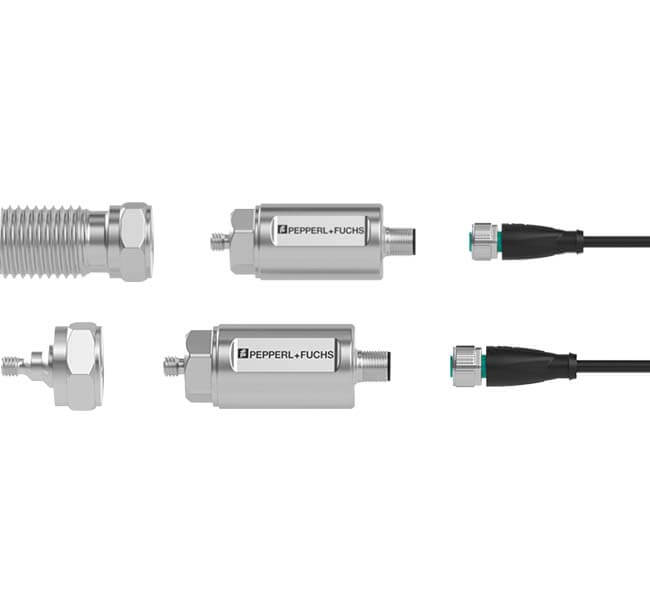
Quality Standards
We are committed to delivering high-quality products and services, ensuring customer satisfaction and trust.
Customized Solutions
Our comprehensive consulting services target client goals, resolving pain points with customized, effective solutions.

Inventory Management
We help clients manage inventories effectively, reduce operational risks, and optimize uptime while minimizing costs.